Explore The Different Aspects Of OSHA 10-Hour & OSHA 30-Hour Courses
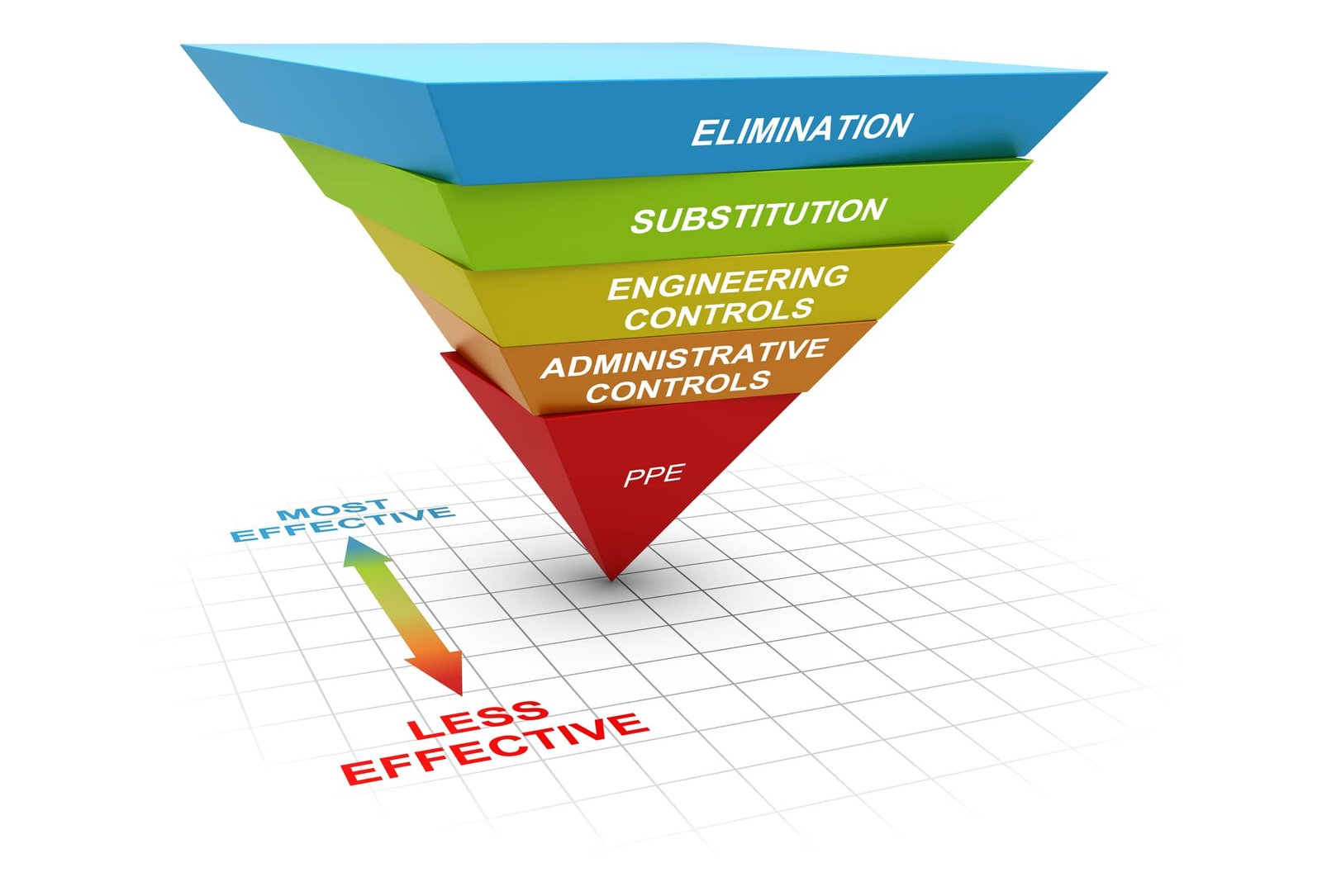
Worker safety is paramount in the construction industry, given its alarming statistics of fatalities and nonfatal incidents. Construction alone accounts for a staggering 21% of all deaths among US workers in 2021. Additionally, there were 2.61 million nonfatal workplace safety incidents reported in the same year, encompassing slips, trips, falls, illnesses, and other injuries. Although this number represents a slight decrease of 1.8% from the previous year, it still underscores the pressing need for stringent safety measures. OSHA’s Outreach Training Programs for Addressing Workplace Safety Concerns In response to these concerning rates of risks and injuries, the US Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has implemented a comprehensive training program tailored for employees in specific fields with one million employees attending these courses every year. The Outreach Training Program comprises two categories: the 10-hour and 30-hour courses, aimed at educating workers on workplace safety and health measures. Despite their shared focus on health and safety, many individuals remain perplexed by the distinction between OSHA 10-Hour and 30-hour courses. Essential Components of OSHA 10-Hour Training The OSHA 10-hour training primarily targets entry-level workers in construction and general industry. It covers essential safety and health information, including an explanation of serious workplace hazards, workers’ rights, employer responsibilities, and procedures for filing OSHA complaints. The training also provides insights into inspection priorities and processes, the function of OSHA, workers’ rights, and basic safety requirements such as personal protective equipment (PPE), health hazards, cranes, ladders, stairways, fire protection, and exposure to lead and asbestos. Essential Components of OSHA 30-Hour Training The General Industry OSHA 30-hour training, on the other hand, is much more comprehensive and is designed for safety directors, foremen, and supervisors. This course covers the same material as the 10-hour course but delves deeper into topics such as OSHA standards, safety and health hazards, and regulations. It also provides extensive training on various types of PPE, fire protection, hazard recognition, accident prevention, and safety requirements in diverse situations like ladders, excavation sites, construction sites, confined spaces, electrical hazards, hazardous materials, and more. Overall, OSHA training plays a crucial role in raising awareness among workers, helping them avoid occupational injuries, illnesses, and fatalities, and enhancing job prospects and opportunities for career advancement in the construction industry. Understanding The Differences Between OSHA 10-Hour And OSHA 30-Hour Training Courses OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30-Hour courses stand out as vital training programs designed to enhance workplace safety measures and educate workers on health hazards. Despite their shared goal of promoting safety, several key distinctions set these courses apart. So, here are some of the key factors that keep both of the courses apart; Duration Difference Between OSHA 10-Hour vs. OSHA 30 The numerical designation in OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30-Hour reflects the duration of the curriculum. OSHA 10-Hour courses encompass 10-Hours of instructional time, inclusive of quizzes, tests, and breaks. In contrast, OSHA 30-Hour is three times as long, requiring 30-Hours of instructional content. This difference in length allows OSHA 30-Hour to cover a broader range of topics in greater depth compared to OSHA 10, making it more suitable for individuals with supervisory responsibilities and a need for comprehensive safety training. Distinguishing the Target Audience for OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30 The disparity in course length reflects the differing target audiences. OSHA 30-Hour is tailored for workers with supervisory roles like supervisors, managers, engineers, site leads, and safety specialists. Conversely, OSHA 10-Hour is designed for individuals responsible only for themselves, such as entry-level workers in construction and general industry. This distinction ensures that each course caters to the specific needs and responsibilities of its intended audience, providing relevant and comprehensive safety training. Comparing OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30-Hour Course Content Both OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30-Hour courses commence with an Introduction to OSHA, offering foundational knowledge on the organization’s purpose, significance, and enforcement of workers’ rights and employer responsibilities. However, the curriculum diverges based on industry and level. OSHA 10-Hour primarily emphasizes mandatory topics, allocating a smaller portion of time to elective topics, thus providing a generalized overview of workplace hazards. Conversely, OSHA 30-Hour delves deeper into both mandatory and elective topics, offering comprehensive coverage of common hazards and a broader understanding of safety regulations. Additionally, OSHA 30-Hour incorporates a mandatory module on Managing Safety and Health, imparting critical skills and responsibilities for supervisors, such as job site inspections, accident prevention programs, and hazard identification. This difference ensures that OSHA 30-Hour provides more detailed and targeted training suitable for individuals with supervisory roles. Assessing OSHA Training Requirements For most individuals, the choice between OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30-Hour hinges on their job responsibilities. Workers with supervisory roles necessitate the 30-hour version, while those without oversight responsibilities can opt for the 10-hour course. However, certain jurisdictions or employers may impose specific requirements mandating either course, necessitating careful consideration before enrollment. Understanding one’s role and any regulatory or employer mandates is crucial in determining which course is appropriate, ensuring compliance with safety standards and addressing job-specific training needs. Necessity of OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30-Hour Concurrently While individuals may eventually undertake both courses over their careers, specific circumstances may warrant clarification. OSHA 10-Hour does not serve as a prerequisite for OSHA 30, and individuals can directly enroll in the latter course as per their job requirements. Similarly, if an individual possesses an OSHA 30-Hour certification, it typically fulfills the OSHA 10-Hour requirement, albeit subject to state regulations regarding renewal frequency. Understanding this distinction is crucial to avoid redundant training and ensure compliance with relevant safety standards. However, individuals should verify state-specific regulations and employer policies to ascertain whether holding both certifications is necessary for their particular roles or jurisdictions. By clarifying these requirements, individuals can streamline their training efforts and focus on obtaining the most relevant certification for their career advancement and safety compliance needs. Securing OSHA Certifications through Authorized Providers OSHA does not directly administer Outreach courses but authorizes third-party training providers to conduct them. These providers offer online courses, enhancing flexibility and
Read More